

| Mineral Name | Actinolite |
| First Discovered | Prehistoric, exact year unknown |
| Nickel-Strunz Classification | 09.DE.10 |
| Dana Classification | 66.01.03a.02 |
| ICSD | 24900 |
| Mineral Group | Silicates - Inosilicate in the Asbestos Group |


| Cleavage | Perfect |
| Colour(s) | Green, Green black, Gray green, Black |
| Specific Gravity | 3.04 |
| Diaphaneity | Translucent to Transparent |
| Fracture | Splintery - Thin, elongated fractures produced by intersecting good cleavages or partings |
| Mohs Hardness | 5.5 |
| Luminescence | Non-fluorescent |
| Luster | Vitreous |
| Streak | White |
| Habit(s) | Bladed to Fibrous to Radial |
| Radioactivity | Non-radioactive |
| Magnetism | Non-magnetic |

The following health hazards should be noted when handling actinolite:
 |
BIOHAZARD Actinolite can cause asbestosis, lung cancer, and both pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma. |

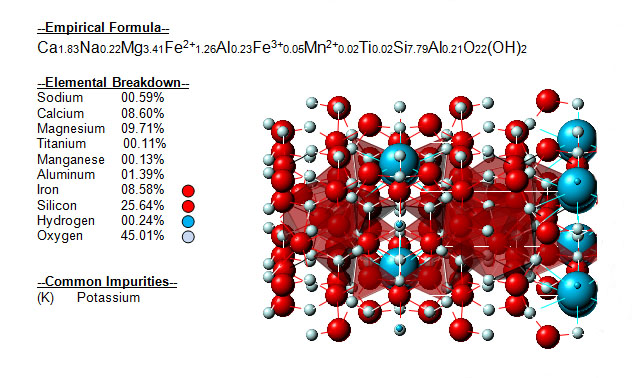
The following image shows the elemental breakdown of the mineral actinolite along with the mineral crystal structure.

| Crystal System | Monoclinic | |
| Class | Prismatic | |
| Axial Ratios | a : b : c = 0.5436 : 1 : 0.2917 | |
| Twinning | simple or lamellar, common parallel | |
| Optical Data Type | Biaxial (-) | |
| Pleochroism (x) | Pale yellow | |
| Pleochroism (y) | Pale yellow, Green | |
| Pleochroism (z) | Pale green, Deep greenish blue | |
| RL Values | nα = 1.613 - 1.646 nβ = 1.624 - 1.656 nγ = 1.636 - 1.666 |  |
| 2V | Measured: 79° to 86°, Calculated: 78° to 82 | |
| Max Birefringence | δ = 0.023 (See colour chart at right) | |
| Surface Relief | Moderate | |
| Dispersion | r < v |

Actinolite can be referenced in certain current and historical texts under the following seven names:
The mineral actinolite can be translated into the following select languages:
| Arabic | الأكتينوليت | Bulgarian | Актинолит | Chinese (Sim) | 阳起石 |
| Croatian | aktinolit | Czech | Aktinolit | Danish | actinolit |
| Dutch | Actinoliet | Esperanto | Estonian | aktinoliidi | |
| Finnish | Aktinoliitti | French | Actinote | German | Aktinolith |
| Greek | Hebrew | אקטינוליט | Hungarian | Aktinolit | |
| Italian | Japanese | 緑閃石 | Korean | 악 티노 | |
| Latin | Aktinolith | Lithuanian | aktinolitas | Norwegian | |
| Persian | اکتینولیت | Polish | Aktynolit | Portuguese | Actinolita |
| Romanian | actinolit | Russian | Актинолит | Slovak | Aktinolit |
| Spanish | Actinolita | Swedish | Aktinolit | Tagalog | |
| Turkish | aktinolitin | Ukrainian | Актиноліт | Vietnamese |

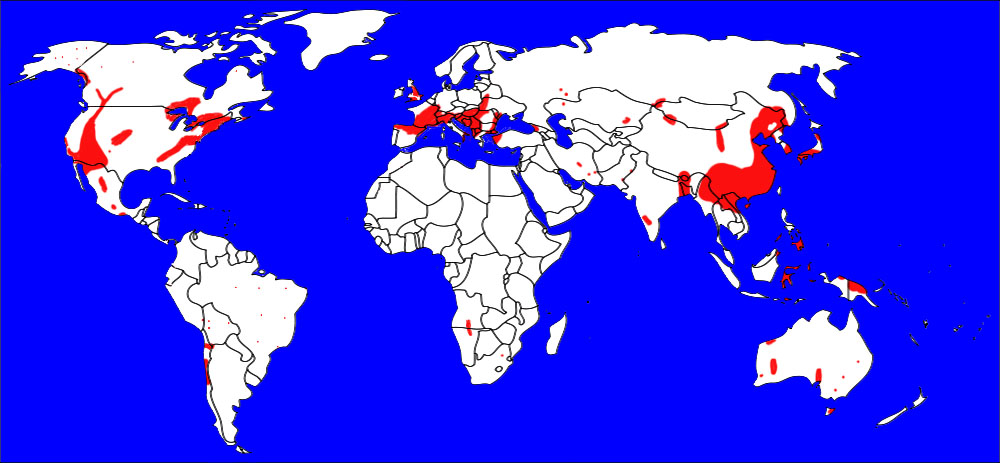
Actinolite can be found in many places around the world. The map below shows major documented concentrations of actinolite:

 |
The MIROFOSS database offers free printable geological identification tags for personal and non-profit use. These tags can be used to properly identify mineral samples in your collection. -Click here- to download a full size jpeg image for a actinolite identification tag; which can be printed on paper or used with a plastic laser printer. |
 |
What's this? What can I do with it? |

| Crystallography | Hawthorne, F. C. and Oberti, R. (2006): On the classification of amphiboles. Canadian Mineralogist 44, 1-21. |
| History | Mineralogical Record: 29: 169-174. |
| History | Canadian Mineralogist (1983) 21: 173. |
| Geographical Data | Mindat.org. Retrieved on 2012-07-30 |
| Physical Identification | Webmineral.com. Retrieved on 2012-07-30 |
| July 30, 2012 | The last time this page was updated |
| ©2017 MIROFOSS™ Foundation | |
 |